A Beginner's Guide to Color Mixing
Ever stare at a wall of paint tubes and feel... lost? Mixing your own colors can seem like wizardry, but it's really just a bit of science and a lot of fun. Here's how to go from being a paint-consumer to a color-creator.

The Basics: What is Color, Anyway?
Why Bother Mixing Colors?
Learning to mix color is the single biggest skill you can learn as a painter. It builds confidence and lets you create more personal, expressive art. 1 It's a hands-on process where you learn exactly how different paints behave and interact with each other. 3
Using pre-mixed colors from a tube makes you a consumer, limited by a manufacturer's choices. Mixing your own colors makes you a creator, which is a big step toward finding your artistic identity. You aren't just making green, you're making your unique green, one that perfectly captures a specific mood or feeling. 3
The Color Wheel: Your New Best Friend
The artist's color wheel is your essential map. It helps you understand the relationships between colors and guess how they'll act when mixed. 5 The wheel is built up systematically, starting with the most basic colors.

Primary Colors (Red, Yellow, Blue)
The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue. They're the foundation for all other colors. 6 You can't create them by mixing other colors, but in theory, you can make every other color from them. 7 On the color wheel, they form a perfect triangle. 5
Secondary Colors (Orange, Green, Purple/Violet)
When you mix any two primary colors, you get a secondary color. 5 These are placed on the wheel right between the two primaries that made them. The recipes are simple:
- Red + Yellow = Orange 7
- Yellow + Blue = Green 8
- Blue + Red = Purple (or Violet) 7
With these, the color wheel now has the six colors of the rainbow, forming a balanced structure. 7
Tertiary Colors
Tertiary colors are the shades that bridge the gap between primary and secondary colors. 6 You make them by mixing a primary color with a secondary color next to it. 2 Their names tell you what they're made of, like red-orange or blue-green. 2 These six colors complete the standard 12-color artist's wheel. 8
Hue, Saturation, and Value: The Big Three
Color isn't flat, every color has three distinct parts, Hue, Saturation, and Value. Knowing these is the key to mixing colors that create depth and make your paintings look interesting. 12
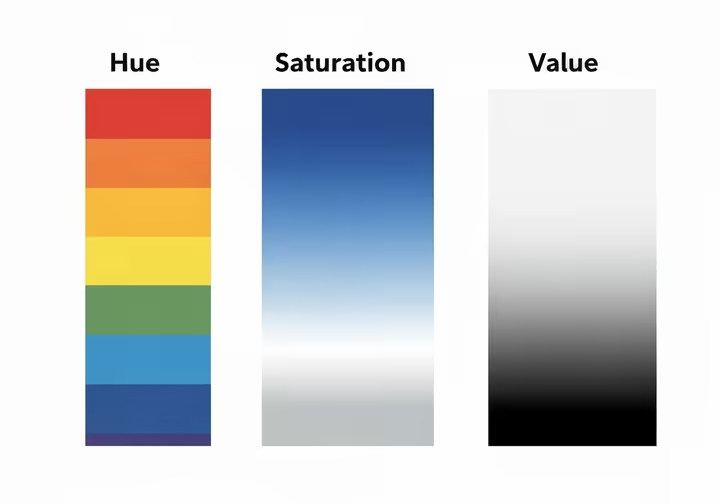
Hue: The Name of the Color
Hue is the easy one, it's just the name of a pure color on the wheel, like red, yellow, or blue. 12 It's the base color your eye identifies first. 6 The hue of a raspberry is red, and the hue of a lime is green. 6
Saturation (or Chroma): The Purity of a Color
Saturation, also called chroma, refers to how intense or pure a color is. 5 A color straight from the tube is at its highest saturation, super vibrant and punchy. A low-saturation color is more muted and calm. 5
You can lower a color's saturation (desaturate it) in a few ways:
- Mix with its Complementary Color: The best way to dull a color is to add a tiny bit of its opposite on the color wheel. Adding a touch of red to a bright green will make it look less intense and more natural. 6
- Mix with Gray: Adding gray creates a "tone" and lowers saturation.
- Mix with Black or White: Adding black or white also reduces saturation, but mostly they just make the color darker or lighter.
Value: The Lightness and Darkness of a Color
Value is simply how light or dark a color is. 5 It's critical for creating the illusion of light, form, and depth. A painting with a good value structure will look 3D and convincing even in black and white. 9 Get the value wrong, and your paintings will look flat, no matter how great the individual colors are. 13
Artists control value by creating tints, shades, and tones:
- Tints: Add white to a color to make it lighter. 6
- Shades: Add black to a color to make it darker. 6
- Tones: Add gray to a color, which affects its saturation and value. 16
The Paints: Mixing in Different Mediums
Color theory is the "what" and "why," but the "how" depends on your paint. Each medium, acrylic, oil, and watercolor, has its own personality and rules. Understanding them is key to successful color mixing.
The paint you use changes how you have to think. Fast-drying acrylics demand quick decisions and layering. Slow-blending oils reward patience and gradual changes. Transparent watercolors require careful planning from the very start.

Table 1: Medium Mixing Characteristics at a Glance
| Property | Acrylics | Oils | Watercolors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying Time | Fast (minutes) | Slow (hours to days) | Fast (minutes) |
| Consistency | Varies (fluid to heavy body) | Buttery, thick | Fluid, thin |
| Opacity | Generally Opaque | Varies (transparent to opaque) | Transparent |
| Cleanup | Water | Solvents (e.g., turpentine) | Water |
| Key Mixing Method | Layering, Wet-on-Wet | Blending, Wet-on-Wet | Glazing, Wet-on-Wet |
| Lightening Method | Add White Paint | Add White Paint | Add Water |
Acrylics: Fast and Furious
The main challenge with acrylics is their fast drying time. 16 A thin layer can dry in minutes, which is great for artists who work quickly in layers but tough for those who need more time to blend. 17
To manage acrylics, you can use a few techniques:
- Palette Mixing: Mix colors on the palette before you paint. This is great for flat areas of color, but the paint on your palette will dry fast. 16
- Wet-on-Wet Blending: Apply wet paint onto an already wet area on the canvas. This lets you blend colors before they dry, perfect for soft gradients in skies. 16
- Layering: Since acrylics dry so quickly, you can easily build up colors in thin layers. Paint a layer, wait a few minutes, and paint another right on top. 17
To slow down the drying time, you have options:
- Acrylic Retarders: These are additives you mix into the paint to slow down drying and give you more time to blend. 16
- Spray Bottle: Keep a spray bottle of water handy to mist your palette and keep the paints wet longer. 16
- Stay-Wet Palette: A special palette with a damp sponge underneath parchment-like paper. It keeps your paints moist from below for a much longer time. 16
Oils: Slow and Steady
Oil painting is a totally different experience, thanks to its slow-drying, buttery goodness. 20 Its slow drying time is its greatest strength, giving you hours or even days to blend, soften, and adjust colors on the canvas. This makes it perfect for creating subtle gradients and realistic effects.
For oils, it's best to mix on your palette with a palette knife to create clean batches of color without ruining your brushes. 20 A key rule is to always mix from light to dark. Start with a light color (like white) and slowly add tiny amounts of a darker color, since dark paints are much stronger. 20
Watercolors: The Transparent Touch
Watercolors are totally different because they're transparent. 23 In watercolor, the white of the paper is your only source of white and light. You can't just paint over mistakes because the layers underneath will always show through.
This transparency gives you three main ways to mix color:
- On the Palette: The simplest method. Mix pigments with a wet brush in your palette before putting them on the paper. 23
- On the Paper (Wet-on-Wet): First, wet the paper with clean water or a light color. Then, drop in other wet colors and watch them flow and mingle together for soft, unpredictable effects. 23
- Layering (Glazing): This is optical mixing. Paint a thin, transparent layer of color (a glaze) over a completely dry area. The eye mixes the colors for you, creating a unique glow. For example, a blue glaze over a dry yellow layer will look green. 23
Color Recipes
Here are some basic recipes for common colors. Think of them as starting points... your exact results will vary based on the specific paints you use.
Table 2: Essential Color Mixing Recipes
| Target Color | Recipe 1 | Recipe 2 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orange | Red + Yellow | A vibrant, warm secondary color. | |
| Green | Yellow + Blue | A cool secondary color. The type of green depends heavily on the bias of the yellow and blue used. | |
| Purple/Violet | Blue + Red | A cool secondary color. Can be difficult to keep vibrant; use a cool red and a warm blue. | |
| Basic Brown | Red + Yellow + Blue | Red + Green | A versatile, low-saturation color. Mixing complements creates nuanced browns. |
| Chromatic Black | Ultramarine Blue + Burnt Umber | A rich, deep black that is more dynamic than tube black. | |
| Chromatic Gray | Red + Green + White | Blue + Orange + White | A neutral created by mixing complements, then lightened with white. More harmonious than black + white. |
Mixing Browns
Brown is a whole family of earthy tones, not just a single color. In color theory, it's a low-saturation color, usually a dark orange. 27 There are two main ways to mix a range of natural-looking browns.
- Recipe 1: Mix Complementary Colors. The most versatile way to make brown is to mix a pair of complementary colors (opposites on the color wheel). 28 Each pair contains all three primaries, so they neutralize each other into a brown or gray.
- Red + Green: Creates a rich, warm, earthy brown.
- Blue + Orange: Creates a cooler, more muted brown.
- Yellow + Purple: Creates a warmer, golden or tan brown. 28
- Recipe 2: Mix the Three Primaries. A direct mix of red, yellow, and blue will also make brown. 28 By changing the amounts of each, you can create an infinite variety of browns.
To make lighter browns like tan, add white (for acrylics/oils) or water (for watercolor). To make darker browns, add more of the darker color in your mix (like blue or red) or a bit of a mixed black. 27
Mixing a Better Black
Black paint straight from a tube can look flat and lifeless in a painting. A mixed "chromatic black" is much more dynamic because it contains hints of other colors that help it fit in with your artwork. 31

- Classic Recipe: Ultramarine Blue + Burnt Umber. One of the best recipes for a deep, rich black is mixing Ultramarine Blue and Burnt Umber. 31 Burnt Umber is basically a dark orange, which is blue's complement. Together, they create a very dark neutral. By adjusting the amounts, you can make a black that's slightly cool or slightly warm. 31
Mixing Skin Tones
Mixing believable skin tones seems hard, but you can break it down into a simple process. The trick is to see skin as a surface with lots of different subtle colors, not just one "flesh" color. Careful observation is more important than any rigid formula. 18

- Step 1: Create a Base Tone. Instead of mixing a new color for every part of a face, start by mixing a versatile mid-tone base color. 32 A common recipe for a light Caucasian skin tone is Yellow Ochre + Cadmium Red + Titanium White. 33
- Step 2: Adjust the Base. You can tweak this base color to match all kinds of skin tones. 33 For darker tones, add small amounts of Burnt Sienna or Burnt Umber. To make areas warmer (like cheeks), add more red. For cool shadows, a tiny bit of blue or violet can work wonders. 18
- Step 3: Mix Shadows and Highlights. Don't use black paint to darken skin tones, it creates a dead, muddy look. 18 For highlights, add more white or a pale yellow. For shadows, add a cool color to your base tone, like Ultramarine Blue, purple, or even a touch of green. 25
Mixing Interesting Grays
Like with black, mixing your own "chromatic gray" is way better than just combining black and white. A chromatic gray has subtle hints of color that make it feel more organic and harmonious within your painting. 37
- Recipe: Mix Complementary Colors + White. The best way to make a beautiful gray is to mix a pair of complementary colors and then add white. 38
- Start by mixing two complements, like Cadmium Red and Viridian Green, until they form a dark, muddy neutral.
- Slowly add Titanium White to this mix. The resulting gray won't be flat, it'll be a complex neutral that leans slightly reddish or greenish.
Experimenting with different pairs (Blue + Orange, Yellow + Purple) will give you a wide range of beautiful, complex grays. 39
Next Level Tips
Once you've got the basics down, you can start using some more advanced ideas. These tips help you think about how colors work together to create a powerful painting.
Organize Your Palette!
A messy palette leads to muddy colors. Simple as that. A clean, logically organized palette is an essential tool for creating predictable, clean color mixes. 21
Lay your paints out in the same consistent order every time, maybe like the colors of the rainbow (yellows, reds, blues, etc.). 41 This builds muscle memory so you can grab colors without thinking. Put your white off by itself so it stays clean, and leave the center of the palette open for mixing. 21
The Limited Palette
It sounds weird, but using fewer colors is one of the fastest ways to improve your color harmony and mixing skills. 42 A limited palette typically uses just three to five colors plus white. This forces you to mix everything you need from a small set of paints.
There are big benefits to this approach:
- Automatic Color Harmony: Because every color in the painting comes from the same few parent colors, they all naturally look good together. 42
- Become a Mixing Master: Working this way forces you to get really good at mixing. You'll learn how to create a huge range of colors from just a few key paints. 42
- Fewer Decisions: With fewer colors to choose from, you can focus more on other important things like composition and value. 42

A famous example is the Zorn Palette, used by painter Anders Zorn. It has only four colors, Yellow Ochre, Cadmium Red, Ivory Black, and Titanium White. 43 It has no blue, but the Ivory Black has a bluish tint, so it can be mixed to make cool grays, blues, and even earthy greens. 44
The Real Secret: Color Temperature and Bias
This is maybe the most important concept for avoiding muddy colors. You need to understand color temperature and, more specifically, color bias. Warm colors (reds, oranges) seem to advance, while cool colors (blues, greens) tend to recede. 45
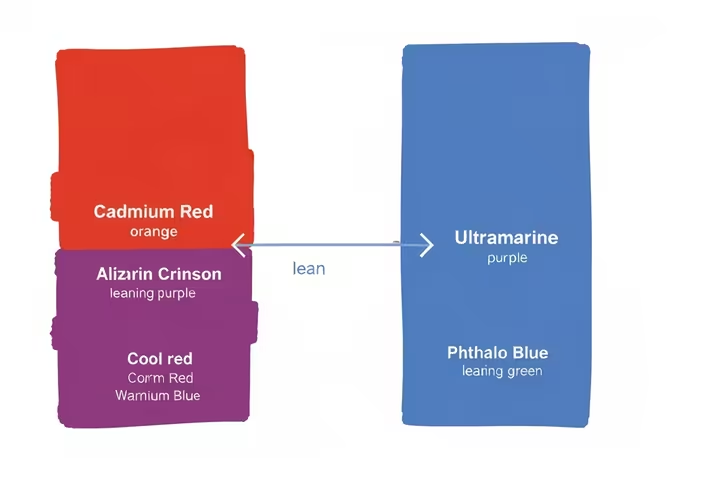
But here's the real secret, every single tube of paint has a color bias. This means it leans towards another color on the color wheel. 46 No red pigment is perfectly pure red.
- A warm red (like Cadmium Red) leans toward orange.
- A cool red (like Alizarin Crimson) leans toward purple. 45
- A warm blue (like Ultramarine Blue) leans toward purple.
- A cool blue (like Phthalo Blue) leans toward green. 47
This hidden bias is the key to mixing clean, vibrant colors. The rule is simple, to mix a bright secondary color, use two primaries that lean toward each other.
- For a Vibrant Green: Mix a cool yellow (leans blue) with a cool blue (leans yellow). For example, Lemon Yellow + Phthalo Blue. Neither has a hidden red bias. 24
- For a Dull Green: Mix a warm yellow (leans red) with a warm blue (leans red). For example, Cadmium Yellow + Ultramarine Blue. Because both paints have a hidden red bias, you're accidentally mixing in red, green's complement. This automatically dulls the green, giving you a more olive tone. 47
A Handy Shortcut: The Magic Palette
If you want a visual cheat sheet, the Magic Palette Color Mixing Guide can help. 48 It's not a technique, it's an actual product, a pre-printed chart that shows you what happens when you mix a specific set of common artist's paints. 49
The guide is usually a grid showing what you get when you mix each color with every other color. It lets you see the result before you waste expensive paint. Think of it as a valuable educational shortcut, not as a replacement for the essential hands-on practice of actually mixing. 48
Works cited
- COLOUR MIXING FOR ARTISTS - Colour Mixing Tutorials, https://colourmixingtutorials.com/colour-mixing-for-artists/
- Color Theory And Why It Matters in Art - Jenna Rainey, https://jennarainey.com/color-theory-and-why-it-matters-in-art/
- Montessori Color Mixing Activity: Exploring One Color at a Time, https://montessori-art.com/montessori-color-mixing-activity-exploring-one-color-at-a-time/
- Look, Listen, Learn. Mixed-Up Color Mixing - NAEYC, https://www.naeyc.org/resources/pubs/tyc/dec2018/mixed-up-color-mixing
- A BEGINNER'S GUIDE TO COLOR THEORY FOR CONCEPT ARTISTS, https://masterclasses.iamag.co/pages/a-beginners-guide-to-color-theory-for-concept-artists
- Color Theory for Absolute Beginners - Trembeling Art, https://trembelingart.com/color-mixing-absolute-beginners/
- 5 Types of Watercolor Charts - Type 3: Color Wheel - Susan Chiang, https://susanchiang.com/blog/watercolor-charts-type-3-color-wheel
- How To Make Your Own Artist Color Wheel - Zen Art Supplies, https://shop.zenartsupplies.co/blogs/toolkit/artist-color-wheel
- Color Theory for Digital Artists | Art Rocket - CLIP STUDIO PAINT, https://www.clipstudio.net/how-to-draw/archives/161372
- A Beginners Guide To Color Theory - Specht & Co. Creative Studio, https://www.spechtand.co/blog/a-beginners-guide-to-color-theory
- Color wheel | Definition, Art, & Facts | Britannica, https://www.britannica.com/science/color-wheel
- How to Understand Value and Why it Matters - Learn to Paint Podcast, https://www.learntopaintpodcast.com/blog/how-to-understand-value-and-why-it-matters
- Three Components of Color: The Expert Guide 2021 - Virtual Art Academy, https://www.virtualartacademy.com/three-components-of-color/
- What is the difference between Hue Value and saturation....? : r/ArtistLounge - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/ArtistLounge/comments/1c8wiho/what_is_the_difference_between_hue_value_and/
- Hue, Value, Saturation | learn., https://learn.leighcotnoir.com/artspeak/elements-color/hue-value-saturation/
- How to Mix Acrylic Paints: Artist's Guide to Creating Colors | Nova ..., https://novacolorpaint.com/blogs/nova-color/mix-colors-for-acrylic-painting
- Beginner's Guide to Acrylic Painting Techniques - Lori Oswald - The Outdoorsy Artist, https://theoutdoorsyartist.com/beginner-acrylic-painting-techniques/
- An Easy Method for Mixing Skin Tones with Acrylic Paint - Craftsy, https://www.craftsy.com/post/mixing-paint-skin-tones/
- How to manage your palette - Artists & Illustrators, https://www.artistsandillustrators.co.uk/how-to/acrylic/how-to-manage-your-palette/
- Oil Paint Mixing Guide - Understanding The Process ..., https://shop.zenartsupplies.co/blogs/toolkit/artists-colour-mixing-tips-for-oils
- HOW TO ORGANIZE A PALETTE AND MIX COLORS | The Painted Canvas, https://www.sgtarr.com/blog/131457/how-to-organize-a-palette-and-mix-colors
- shop.zenartsupplies.co, https://shop.zenartsupplies.co/blogs/toolkit/artists-colour-mixing-tips-for-oils#:~:text=Start%20out%20with%20a%20generous,hue%20to%20the%20lighter%20one.
- How To Mix Watercolors: Three Approaches – Greenleaf & Blueberry, https://www.greenleafblueberry.com/blogs/news/how-to-mix-watercolors-3-approaches
- The Essential Guide to Watercolor Mixing, https://www.watercoloraffair.com/the-essential-guide-to-watercolor-mixing/
- Watercolor Skin Tone Tutorial: How to Mix Realistic Flesh Colors ..., https://www.watercoloraffair.com/watercolor-skin-tone-tutorial-how-to-mix-realistic-flesh-colors/
- 1.4 mechanics of mixing watercolor - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mT3ZwNKquDQ
- What Colors Make Brown? - Michele Clamp Art, https://micheleclamp.com/what-colors-make-brown/
- What Colours Make Brown? How To Mix Your Paint | Pinot ..., https://www.pinotandpicasso.uk/what-colours-make-brown-how-to-mix-your-paint/
- How to Make Brown Paint in 4 Steps - 2025 - MasterClass, https://www.masterclass.com/articles/how-to-make-brown-paint
- thevirtualinstructor.com, https://thevirtualinstructor.com/blog/what-colors-make-brown-how-to-mix-browns#:~:text=How%20to%20Mix%20Brown%20%E2%80%93%20The,%2C%20when%20mixed%2C%20make%20brown.
- How to make black paint by mixing colours - Atelier de la Galerie ..., https://atelier-de-peinture.com/how-to-make-black-paint-by-mixing-colours/
- Hello everyone! Please help me with the skin tones : r/oilpainting - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/oilpainting/comments/1hb59ur/hello_everyone_please_help_me_with_the_skin_tones/
- How to mix and paint skin tones - color mixing | Tim Gagnon Studio, https://timgagnon.com/overall-skin-tone-color-mixing/
- Mixing Skin Tones – Simplified by Susan Patton, https://www.oilpaintersofamerica.com/2024/09/mixing-skin-tones-simplified/
- Colour-Mixing Recipe For Realistic Skin Tones | DeSerres, https://www.deserres.ca/blogs/all-articles/colour-mixing-recipe-for-realistic-skin-tones
- 12 Steps on How to Paint Realistic Skin Tones in Your Acrylic Portrait, https://realisticacrylic.com/12-steps-on-how-to-paint-realistic-skin-tones/
- www.reddit.com, https://www.reddit.com/r/painting/comments/1bix6p4/how_do_you_create_chromatic_gray/#:~:text=Chromatic%20gray%20just%20means%20a,it%20to%20a%20grayish%20color.
- How do you create 'chromatic gray'? : r/painting - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/painting/comments/1bix6p4/how_do_you_create_chromatic_gray/
- CHROMATIC GREY SCALES – Week 1b - Colour, Light and Space Workshop, https://colourlightspaceblog.wordpress.com/2017/05/02/chromatic-grey-scales-week-2/
- Stage 4 - Mixing colour - Poly-chromatic greys - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Nw5T2eRm2SM
- Tips for Setting up an Oil Painting Palette - Jackson's Art Blog, https://www.jacksonsart.com/blog/2023/09/11/tips-for-setting-up-an-oil-painting-palette/
- The Benefits of Using a Limited Colour Palette — Louise De Masi ..., https://www.louisedemasi.com/tips/2023/11/6/benefits-of-using-a-limited-colour-palette
- A Guide To The Zorn Palette - Artists & Illustrators, https://www.artistsandillustrators.co.uk/how-to/art-theory/the-zorn-palette-an-essential-guide/
- Colour Mixing: Exploring the Zorn Palette - Jackson's Art Blog, https://www.jacksonsart.com/blog/2021/02/02/colour-mixing-exploring-the-zorn-palette/
- Understanding Color: Temperature — Charlene Collins Freeman Art, https://charlenecollinsfreeman.com/blog-montauk/2018/11/28/understanding-color-temperature
- Understanding Color Temperatures and Undertones: A Comprehensive Guide - Jenna Rainey, https://jennarainey.com/understanding-color-temperatures-and-undertones-a-comprehensive-guide/
- How to Mix Colours When Painting in Acrylics - Blue Beach House Art, https://bluebeachhouseart.com/how-to-mix-colours-when-painting-in-acrylics/
- Magic Palette, https://www.magicpalette.us/
- www.magicpalette.us, https://www.magicpalette.us/#:~:text=Personal%20Color%20Mixing%20Guide,instructions%20on%20the%20reverse%20side.
- Magic Palette Studio Color Mixing Guide - Art Supply Warehouse, https://www.artsupplywarehouse.com/products/magic-palette-studio-color-mixing-guide%7CMGP5841.html
- Mixing acrylic paint formula to get RGB result : r/minipainting - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/minipainting/comments/1jmifzj/mixing_acrylic_paint_formula_to_get_rgb_result/
- Top 5 Acrylic Paint Color Mixing Mistakes (and How to Fix Them) - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9x6eY7SYxZ0
- Color Mixing Guide | Golden Artist Colors, https://goldenartistcolors.com/resources/color-mixing-guide
- Oil Paint Mixing Guide - Ran Art Blog, https://ranartblog.com/blogarticle04.html
- How to Formulate Hair Color | Hair Color Formula Guide - Simply Organic Beauty, https://www.simplyorganicbeauty.com/hair-color-formulation-guide/
- How to Measure Hair Color and Developer: Guide for Stylists - GlossGenius, https://glossgenius.com/blog/how-to-measure-hair-color-and-developer
- how to mix hair color with developer at home | 2024 - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q-_ql75w-SU